How Synthetic Data Protect Privacy
How synthetic data protect privacy in AI and data-driven innovation
How Synthetic Data Protect Privacy
Synthetic data are computer-generated data. When generated properly, they preserve the analytic value of real data, but are devoid of sensitive information. This makes them a safer and more ethical alternative to real data. For these reasons, Gartner predicts that by 2030, most AI systems will be trained on synthetic data. In this article, we explore how synthetic data are generated and how they protect privacy.
How are synthetic data generated?
Synthetic data are not collected by empirical means. Instead, they are constructed by algorithms. Most of these algorithms work as follows: first, a probability model is inferred from real data. This model describes all of the data’s intricate patterns. Next, the real data are discarded, leaving only the probability model. Finally, synthetic data are generated by creating new records through the model. The resulting data then have all the patterns of the real data, but their records cannot be linked to real individuals. A simplified version of this process is illustrated in Figure 1.
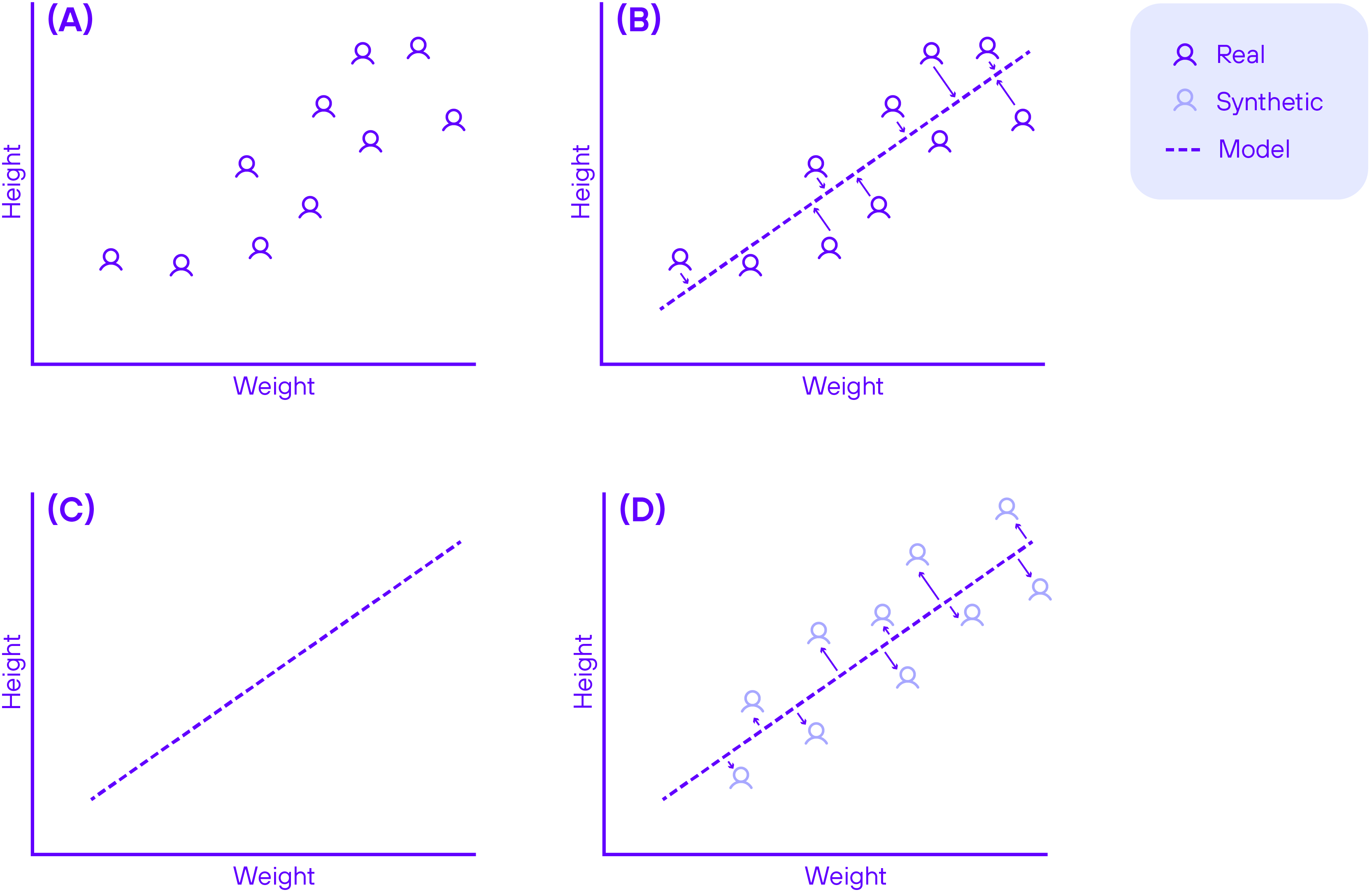 Figure 1. Simplified representation of synthetic data generation. (a) a real dataset is provided. (b) a probability model is inferred from the data. The model describes the patterns of the real data. In this case, it captures the correlation between height and weight. The model is represented by the dashed line. (c) The real data is discarded, leaving only the model. (d) Synthetic data is generated by the model. It has the same correlation between height and weight as the real data. However, no synthetic record has a direct correspondence to any specific real record.
Figure 1. Simplified representation of synthetic data generation. (a) a real dataset is provided. (b) a probability model is inferred from the data. The model describes the patterns of the real data. In this case, it captures the correlation between height and weight. The model is represented by the dashed line. (c) The real data is discarded, leaving only the model. (d) Synthetic data is generated by the model. It has the same correlation between height and weight as the real data. However, no synthetic record has a direct correspondence to any specific real record.
Statistical and mathematical synthetic data methods date back several decades. More recently, generative AI-based methods have emerged. These include simple decision and regression tree models; agent-based models; and clustering-based approaches. The most effective generative AI approaches to synthetic data generation are: generative adversarial networks (GANs), variational autoencoders (VAEs), diffusion models, and transformers. These emerged around 2014. Since then, they have led to a revolution by reaching new levels of realism, privacy protection, and efficiency.
Synthetic data for privacy protection
Synthetic data protect privacy by replacing real data in analyses, software testing, and AI training. Unlike real data, synthetic records are not linked to real individuals. Their use minimizes the storage and processing of personal information. That is why synthetic data are widely used for data protection. The AI Act mentions synthetic data as a preferred datasource in AI development, along with other forms of non-personal data (art. 59.1.b).
Four of the most common use cases are:
- Data mobility. Data protection protocols restrict both internal and external exchange of information. This hinders organizations from unlocking the full value of their data. Synthetic data allow for wider information access, culminating in better analysis and innovation.
- Secondary data usage. Real data is usually collected with a specific purpose and cannot be reused for a different purpose. By contrast, synthetic data can be reused many times without limitations.
- Optimized data management. A study found that 94% of companies suffer from insider data breaches. Often unintentional, these breaches result from improper data storage and access management. Substituting synthetic for real data can drastically reduce the risk of insider data breaches.
- Data retention. Privacy protocols involve restrictions on how long data can be stored for. This hinders longitudinal data analysis. However, time limits do not apply to synthetic data which can be stored overtime and enable new types of analysis.
In an upcoming blog post, we will delve deeper into each of these use cases. See our blog about synthetic data success stories to learn more about the use of synthetic data in real practical applications.
Conclusion
AI and data-driven innovation are improving all facets of life. The dependence of these fields on large amounts of data has raised privacy concerns. Luckily, synthetic data technology facilitates safe information access and exchange. Synthetic data allow privacy and innovation to coexist, enabling society to benefit from AI in a responsible manner.
At Aindo, we are at the forefront of synthetic data technology. Stay tuned to our blog and LinkedIn page to learn more about its advancement.


